Compute Power-Profile for an Activity¶
This example shows how to compute the power-profile of a cyclist for a single activity. We will also show how to plot those information.
# Authors: Guillaume Lemaitre <g.lemaitre58@gmail.com>
# License: BSD 3 clause
print(__doc__)
First, we will load an activity from the toy data set available in scikit-cycling.
We will only select some of interesting information
columns_selected = ['power', 'speed', 'cadence']
ride = ride[columns_selected]
The power-profile is extracted from the ride. By default, the maximum duration corresponds to the duration of the ride. However, to limit the processing, we limit the extraction to 8 minutes.
from skcycling.extraction import activity_power_profile
power_profile = activity_power_profile(ride, '00:08:00')
print('The power-profile is:\n {}'.format(power_profile))
Out:
The power-profile is:
cadence 00:00:01 78.000000
00:00:02 64.000000
00:00:03 62.666667
00:00:04 62.500000
00:00:05 64.400000
00:00:06 64.500000
00:00:07 64.571429
00:00:08 64.625000
00:00:09 64.222222
00:00:10 62.000000
00:00:11 61.909091
00:00:12 62.083333
00:00:13 61.846154
00:00:14 64.928571
00:00:15 60.466667
00:00:16 65.437500
00:00:17 66.000000
00:00:18 65.888889
00:00:19 65.842105
00:00:20 65.550000
00:00:21 66.000000
00:00:22 66.136364
00:00:23 66.391304
00:00:24 66.625000
00:00:25 66.960000
00:00:26 67.307692
00:00:27 67.666667
00:00:28 67.964286
00:00:29 68.103448
00:00:30 68.233333
...
speed 00:07:30 7.607184
00:07:31 7.610104
00:07:32 7.624642
00:07:33 7.627801
00:07:34 7.631033
00:07:35 7.967097
00:07:36 7.971888
00:07:37 7.976606
00:07:38 7.981303
00:07:39 7.986033
00:07:40 7.990848
00:07:41 7.995642
00:07:42 8.000258
00:07:43 8.005011
00:07:44 8.009690
00:07:45 8.014245
00:07:46 8.019255
00:07:47 8.024086
00:07:48 8.029380
00:07:49 8.034599
00:07:50 8.039849
00:07:51 8.045524
00:07:52 7.591794
00:07:53 7.591892
00:07:54 7.591876
00:07:55 7.591501
00:07:56 7.603939
00:07:57 7.616686
00:07:58 7.629561
00:07:59 7.642568
Name: 2014-05-07 12:26:22, Length: 1437, dtype: float64
The power_profile is a pandas Series with multi-index. The additional information (e.g. speed, cadence, etc.) associated with the maximum power extracted are also computed. It is possible to plot those information using pandas. For instance, we will plot only the power information.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
power_profile.loc['power'].plot(title='Power-profile')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Power (W)')
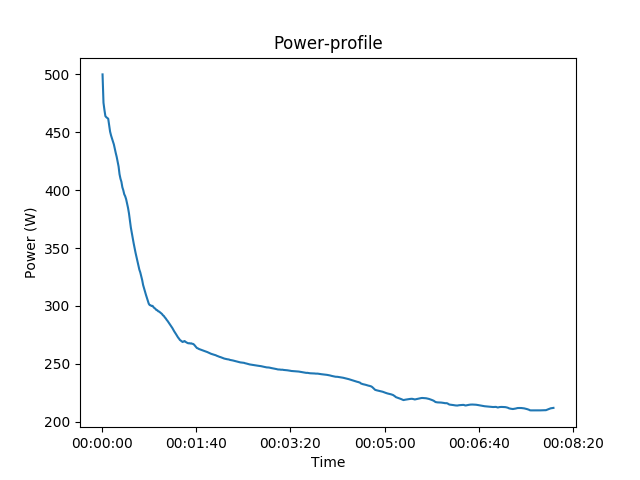
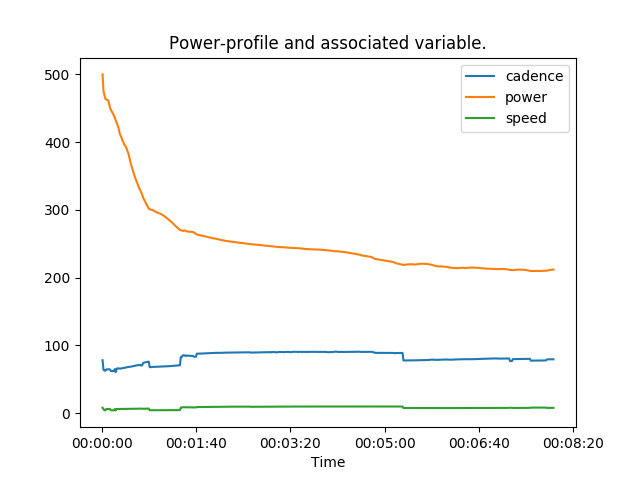
In the same manner, we could plot all information using the pandas API.
power_profile.unstack().T.plot(title='Power-profile and associated variable.')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.171 seconds)