Infer Power using all Forces Applying to a Cyclist¶
This examples shows how we can use a physic model based on all forces applied to a cyclist to infer power produced by a cyclist.
print(__doc__)
# Authors: Guillaume Lemaitre <g.lemaitre58@gmail.com>
# License: BSD 3 clause
We can first grab a file and read all data available
We can use a physical model to infer the power.
from skcycling.model import strava_power_model
power = strava_power_model(ride, cyclist_weight=72)
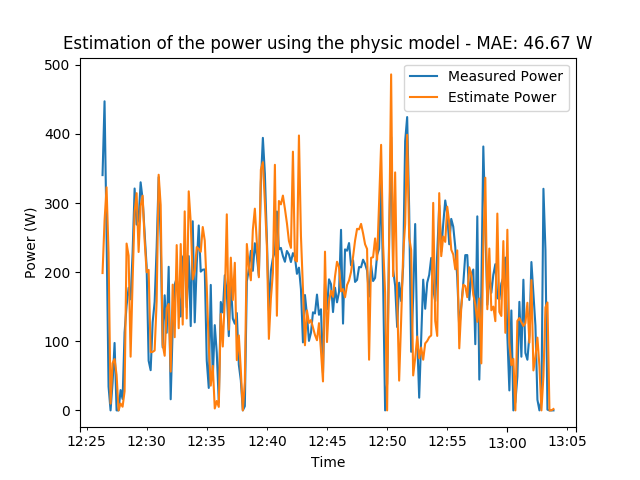
We can plot the measured and estimated power to observe the difference. We can also compute the median absolute error to asses the quality of the estimation. To ease the interpretation, we will first resample the data.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import median_absolute_error
resampling_rate = '10S'
measured_power = (ride['power'].resample(resampling_rate)
.mean()
.rename('Measured Power'))
estimated_power = (power.resample(resampling_rate)
.mean()
.rename('Estimate Power'))
mae = median_absolute_error(measured_power, estimated_power)
measured_power.plot(legend=True)
estimated_power.plot(legend=True)
plt.title('Estimation of the power using the physic model - MAE: {:.2f} W'
.format(mae))
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Power (W)')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.981 seconds)